11159. Breed counting
Several seasons of hot summers and cold
winters have significantly damaged Farmer John's fence for n cows,
which are lined up in a row and consecutively numbered
from 1 to n. Each cow belongs to one of three
breeds: 1 – Holsteins, 2 – Guernseys, 3 – Jerseys.
Farmer John asks you to count the number of cows of each breed within a given
range.
Input. The first line contains two integers n and q (1
≤ n, q ≤ 105).
Each of the next n lines
contains one integer, 1, 2, or 3, which is the breed identifier of the
corresponding cow.
The following q lines describe the
queries, each consisting of two integers a and b (a ≤
b).
Output. For each of the q queries (a, b),
print a line containing three integers — the number of cows of each breed in
the interval from a to b, inclusive.
|
Sample
input |
Sample
output |
|
6 3 2 1 1 3 2 1 1 6 3 3 2 4 |
3 2 1 1 0 0 2 0 1 |
SOLUTION
partial sums
Algorithm analysis
Let’s declare three integer arrays s[i] (1 ≤ i ≤ 3).
The prefix sums for cows of breed i will be stored in the array s[i].
The
answer to the query (a, b) is computed as follows:
·
The number of cows of breed 1 is s[1][b]
– s[1][a – 1];
·
The number of cows of breed 2 is s[2][b] – s[2][a – 1];
·
The number of cows of breed 3 is s[3][b] – s[3][a – 1];
Example
For
the given example, the prefix sum arrays s[i]
(1 ≤ i ≤ 3) will
be as follows:
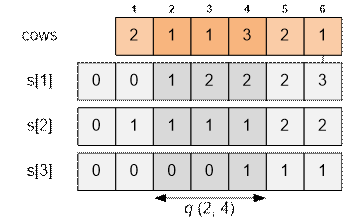
Consider
the query on the interval (2, 4):
·
The number of cows of breed 1 is s[1][4] – s[1][1] = 2 – 0 = 2;
·
The number of cows of breed 2 is s[2][4] –
s[2][1] = 1 – 1 = 0;
·
The number of cows of breed 3 is s[3][4] –
s[3][1] = 1 – 0 = 1;
Algorithm implementation
Declare an array
for storing prefix sums.
#define MAX 100001
int s[4][MAX];
Read the
input data.
scanf("%d %d", &n, &q);
Compute the
prefix sum arrays.
memset(s, 0, sizeof(s));
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &x);
for (j = 1; j <= 3;
j++)
s[j][i] = s[j][i - 1];
s[x][i]++;
}
Process the
q queries sequentially.
for (i = 0; i < q; i++)
{
scanf("%d %d", &a, &b);
printf("%d %d
%d\n", s[1][b] - s[1][a -
1], s[2][b] - s[2][a - 1],
s[3][b] - s[3][a - 1]);
}
Python implementation
import sys
Read the
input data.
n, q = map(int, input().split())
Declare a
list for storing prefix sums.
s = [[0] * (n + 1) for _ in range(4)]
Compute the
prefix sum arrays.
for i in range(1, n + 1):
x = int(input())
for j in range(1, 4):
s[j][i] = s[j][i - 1]
s[x][i] += 1
Process the
q queries sequentially.
for _ in range(q):
a, b = map(int, input().split())
print(s[1][b] - s[1][a - 1], s[2][b] - s[2][a - 1],
s[3][b] - s[3][a - 1])